

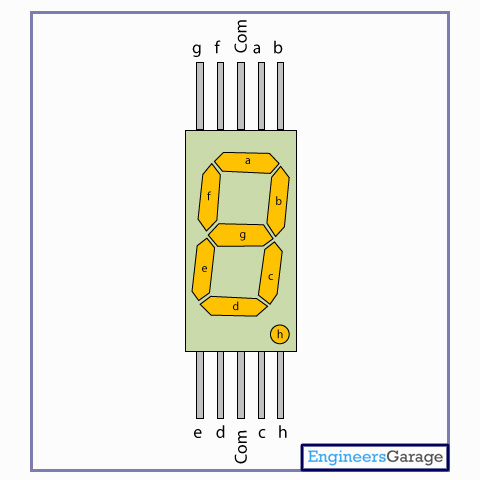
Common cathode means that all the seven cathodes of a 7-segment display are connected together. In seven segment displays, when all the anodes are connected to one point, it becomes a common anode.What is the difference between Common Anode and Common Cathode? When using the seven segments, the common cathode must be grounded. When all the seven cathodes of a 7-segment display are connected together, it becomes common cathode. This allows more electrons to come into the cathode from the anode. As these electrons are used up to the reduction reactions, there will be more electron deficiencies.


Since current is flowing out of the electrode, electrons are flowing in. Reduction reaction takes place on the cathode therefore, there should be electrons. In an electrochemical cell, inside the solution, the cations are attracted to the cathode. However, power will be supplied to all the seven segments.Ĭathode is the electrode where the positive current flows out of the system. Power supply’s positive end is connected to the anode. Therefore, instead of seven anodes, there is only one common anode. In these displays, all the anodes are connected to one point, and it becomes a common anode. They are widely used in digital clocks and meters, etc. This is an electronic display device which shows decimal numerals. Since current flow is in the opposite direction of the electron flow, we see it as current flowing into anode.Ĭommon anode is used in the seven-segment displays. Because of this, electrons flow to cathode from the anode. Therefore, there is electron abundance on the anode compared to the cathode. So when anions come into the anode in the solution, they undergo oxidation and release electrons. Normally, oxidation reactions are taking place on the anode. So from outside circuit, current flows into the anode, which means that the electrons are moving away from the anode. If we take an electrochemical cell as an example, anode can be remembered as the electrode where anions in the electrolytic solutions are attracted. However, for the study purpose and for our easiness, we can remember anode and cathode in relation to their functions, not the structure.Īnode is the terminal where current flows-in from outside. However, for non-rechargeable batteries and light emitting diodes, the anodes and cathodes are permanent. For example, when a rechargeable battery is charged, the positive terminal is the anode, but when the same battery is discharged, cathode becomes the positive terminal. According to the circumstances, an electrode once functioned as a cathode can change to work as an anode. In some equipments, we cannot surely say one as the anode and the other as the cathode. Anode and cathode are defined by this current flow. ‘Current-out’ means current is flowing out of the system. For a device, when we say ‘current-in,’ that means the current is flowing into the system. When the electrons are flowing to one direction, we say current is flowing to the opposite direction to the electrons. In other words, current is carried by moving electrons. When a current is flowing, negatively charged electrons are flowing. Electrochemical cells, cathode ray tubes, and X-ray tubes are some examples where we come across anodes and cathodes. Anode and cathode are necessary for electrical set ups where current flow is involved.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
